Wisdom is the ability to use knowledge and experience to deal with life’s challenges. According to the Berlin wisdom paradigm, it includes lifespan contextualism, value relativism, acknowledgement of uncertainty and strategic humility.
It is an essential part of human well-being. Yet, little work has investigated the link between wise reasoning and a variety of well-being indicators.
The Impact of Smart vs Wise
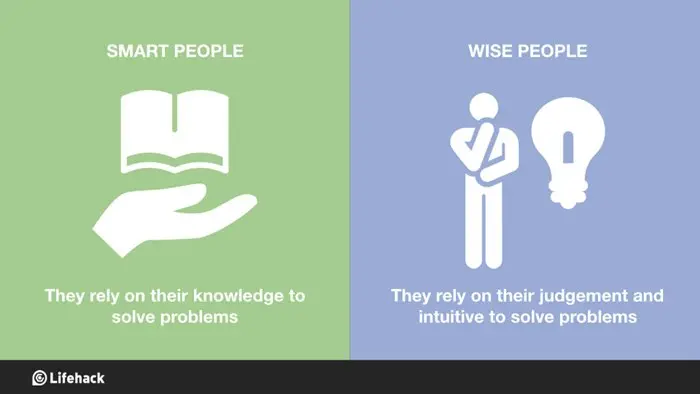
A smart person is someone who knows a lot of information and gets good grades in exams. They are also quick-witted and often enjoy expressing their opinions. However, they don’t always have the right answer to a question.
Unlike smart, wise is a word that refers to people who have experience, knowledge, and good judgment. It is used to refer to people of all ages.
The difference between smart and wise is that smart refers to intelligence whereas wise mainly refers to experience and knowledge.
This is a big difference between the two words because if you have experience, you know more than if you only have theoretical knowledge. Wise is more important than smart in many ways.
Wisdom can be defined as the ability to use your experiences, knowledge, and experience of other people in order to make a decision that is useful for you and your life. It is a skill that can be cultivated through experience, education and self-development.
In addition, wisdom is also more difficult to measure than smarts. Unlike smarts, there is no IQ test that measures wisdom or even a point system to tally experience and person growth.
To explore the relationship between wisdom and well-being, we evaluated a sample of 104 adults (average age: 45 years) who completed a face-to-face laboratory session. In this setting, participants were provided with information about future events and asked to provide their reasoning about these situations (Grossmann et al., 2010).
We found that the ability to reason wisely about social conflicts was associated with a range of well-being indicators, including greater global life satisfaction, greater satisfaction with social relationships, less negative affect in daily life, less tendency to brood, more positive discussion of social conflicts, and longer lifespan. This association was consistent across intergroup and interpersonal scenarios, and when controlling for crystallized cognitive abilities, personality factors, and a variety of socio-economic and demographic characteristics.
The link between wise reasoning and well-being was mediated by age, with the effect of age being stronger among older adults than among younger ones. This is because people in older age are more likely to have life-threatening illnesses, such as cancer, and may have less well-being than younger adults.
Read more:The Top 5 Business Strategies That Will Help Your Business Grow
Smartness
Generally speaking, smartness is a relative term. For some, being smart is about regurgitating facts in a flash, while for others it is about acquiring wisdom. However, it is important to consider how to define and measure smartness, because it can have a big impact on our daily lives.
For starters, it is important to understand the interlinkages between current digitalization, capitalism and urbanization, because these relationships shape Smart City approaches and their impacts on current urban life. A granular understanding of the social, economic and political factors behind the onset, implementation and consequences of smart city technologies can reveal insights into their efficacy and pitfalls.
This is especially true of data-driven and software-mediated Smart City solutions. They can improve urban processes such as planning, service delivery, traffic management and environmental management while enhancing public participation and achieving urban sustainability goals.
To be fair, a number of scholars have recognized the importance of non-technical and bottom-up social and political processes and initiatives in the smart city space. Moreover, the most innovative smart city solution is the one that is able to integrate multiple data sources into a single, holistic view of the city.
Finally, a well-designed smart city is a product of the surrounding context and can only succeed by incorporating the right technologies and social structures. Hence, the triumvirate of human-computer-nature-and-society is a winning combination that should be embraced to achieve urban smartness for all. Lastly, the most important lesson to be learned is that we must all be smarter about how we make decisions and interact with each other.
Intelligence
Intelligence is the ability to make decisions and achieve goals. It is a complex and multidimensional process that can be found in many different types of animals, including humans, and also machines.
The concept of intelligence has been a major topic in science, particularly psychology. Various investigators have tried to define intelligence, with some stressing certain aspects while others emphasize adaptation to the environment.
In addition, some investigators believe that people should be judged based on their reasoning abilities rather than just on the number of IQ points. This is because some of the most important decisions that people make are related to how they perceive the world around them, and the type of information they have access to.
According to multiple intelligence theory, every individual possesses a number of intelligences, which they are able to use at different times and in different ways. This approach has been refined for more than 30 years and is largely accepted by the scientific community.
A person’s level of intelligence affects their daily life and is a key factor in their success and happiness. However, research has shown that the relationship between intelligence and well-being is ambiguous.
One area that psychologists have studied is the differences between fluid and crystallized intelligence. Fluctuating intelligence is the ability to solve new problems without relying on prior knowledge, while crystallized intelligence involves a fixed set of skills and knowledge that individuals build up over time (Sternberg, 1988).
Researchers have also looked at intelligence in terms of how it relates to a person’s social interactions and their decision-making processes. They have found that standard intelligence tests don’t do a good job of measuring this type of thinking.
As a result, scientists are interested in developing and applying intelligence-enhancing methods to improve the well-being of people. For example, psychologists have found that people with high levels of abstract reasoning ability report better health and more satisfying relationships than those who have low scores on this measure.
Wisdom
Wisdom is the ability to make good decisions based on facts and experience. It is also a skill for living in a world that is constantly changing and evolving. It involves a combination of knowledge, experience, and a profound understanding that incorporates tolerance for all the ups and downs that come with life.
Being wise can have a positive effect on your life and the lives of others around you. It helps you develop your relationships and societal skills, allowing you to navigate your life situations in the best way possible.
It can also help you make sense of complicated problems and find solutions that work for you. It can also help you protect yourself from recklessness and hasty decisions that could lead to regret later on.
Researchers are now developing many theories to measure and model wisdom. One theory, for example, suggests that wise people have “rich procedural knowledge in the fundamental pragmatics of life that permits exceptional insight, judgment, and advice about complex and uncertain matters.”
This theory also includes five criteria: rich factual knowledge, an understanding of different life contexts, recognition of and management of uncertainty, an awareness of the relativism of values and priorities, and an appreciation of differences among individuals.
Using this theory, researchers have found that some people are more wise than others. These include those with more experience, those who are older, and those who have better interpersonal relationships.
In addition, being a teacher can have a positive impact on your wisdom. Teaching requires you to be open to the perspectives of your students and be a good listener, qualities that may enhance your wisdom.
Another aspect of wisdom is balance, which is the ability to keep your own needs while also considering the interests and needs of others. Being balanced allows you to take other people’s viewpoints into account and understand their goals, motivations, and desires.
Wise people often act on behalf of the common good, striving for harmony among competing demands and goals. They also strive to make a difference in the lives of others and cultivate their relationships. They are respected and loved by those around them, and they enjoy a high level of satisfaction in their work.