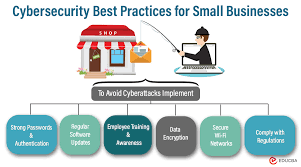
In an increasingly digital world, small businesses are prime targets for cyber threats. The consequences of a security breach can be devastating, ranging from financial loss to damage to the business’s reputation. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures is essential to protect sensitive information and maintain the trust of customers. Here are best practices for small businesses to enhance their cybersecurity posture:
1. Educate Employees: Create a Security-Aware Culture
The first line of defense against cyber threats is a well-informed workforce. Conduct regular cybersecurity training sessions for employees, covering topics such as recognizing phishing attempts, using strong passwords, and understanding the importance of software updates. Fostering a security-aware culture among employees is critical.
2. Use Strong Passwords: Implement Password Policies
Enforce strong password policies to reduce the risk of unauthorized access. Encourage the use of complex passwords that include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Regularly update passwords and consider implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) for an added layer of security.
3. Keep Software Updated: Patch Vulnerabilities
Regularly update operating systems, software, and applications to patch known vulnerabilities. Cybercriminals often exploit outdated software to gain unauthorized access. Enable automatic updates where possible, and regularly check for security patches provided by software vendors.
4. Secure Wi-Fi Networks: Protect Access Points
Ensure that Wi-Fi networks are secured with strong encryption protocols, such as WPA3. Change default router login credentials, use strong passwords for Wi-Fi access, and consider implementing a guest network for visitors. Regularly review and update Wi-Fi security settings.
5. Implement Firewall Protection: Control Network Traffic
Deploy firewalls to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic. A well-configured firewall acts as a barrier against unauthorized access and helps prevent malware and other malicious activities. Consider both hardware and software firewalls for comprehensive protection.
6. Backup Data Regularly: Ensure Business Continuity
Regular data backups are crucial for business continuity in the event of a cyber incident or data loss. Back up essential data regularly and store backups in a secure, offsite location. Test the restoration process periodically to ensure data can be recovered effectively.
7. Encrypt Sensitive Information: Safeguard Data
Encrypt sensitive data, both in transit and at rest. Encryption ensures that even if unauthorized individuals access the data, they cannot decipher it without the encryption key. Implement encryption for emails, stored files, and data transmitted between devices.
8. Limit Access: Least Privilege Principle
Adhere to the principle of least privilege by granting employees access only to the information and resources necessary for their roles. Regularly review and update user access permissions to minimize the risk of insider threats and unauthorized access.
9. Monitor Network Activity: Detect Anomalies
Implement network monitoring tools to detect unusual or suspicious activities. Unusual patterns in network traffic, login attempts, or data access may indicate a potential security threat. Regularly review logs and alerts to identify and respond to anomalies promptly.
10. Create an Incident Response Plan: Be Prepared
Develop a comprehensive incident response plan outlining steps to be taken in the event of a security incident. Clearly define roles and responsibilities, establish communication protocols, and conduct regular drills to ensure a swift and effective response to cybersecurity incidents.
11. Collaborate with Cybersecurity Experts: Seek Professional Guidance
Consider engaging with cybersecurity experts or consultants to assess your business’s security posture. Professionals can conduct vulnerability assessments, provide recommendations, and assist in implementing advanced cybersecurity measures tailored to your business’s needs.
12. Stay Informed: Keep Abreast of Cyber Threats
Cyber threats are continually evolving, and staying informed is crucial for effective cybersecurity. Subscribe to cybersecurity news sources, participate in relevant forums, and attend training sessions to keep abreast of the latest threats and best practices.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is a continuous effort that requires diligence and proactive measures. Small businesses, often seen as easy targets by cybercriminals, can significantly enhance their security posture by implementing these best practices. By educating employees, securing networks, regularly updating systems, and staying vigilant, small businesses can mitigate the risk of cyber threats and build a resilient defense against potential security breaches.